A Tour of IDEELab’s Advanced Machinery: From CNC to 3D Printing
- Katie Lang
- Feb 6
- 4 min read

At the Innovation, Design, and Engineering Education Laboratory (IDEELab), we pride ourselves on having a wide array of cutting-edge tools that bring student and faculty ideas to life. Whether you’re sculpting complex metal parts on a 5-axis CNC mill or welding a student-designed chassis together, our equipment lays the foundation for hands-on innovation. Below, we’ll walk you through each category of machinery, highlighting their key features, typical applications, and how they enhance learning and research at Mississippi State University.

CNC Machines
What Are CNC Machines?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are automated systems that convert digital designs into precisely machined parts. By programming coordinates and tool paths, users can shape materials like metal, plastic, and composites with pinpoint accuracy.
IDEELab's CNC Machines
Haas VF1 CNC Mills (2 Units)
Overview: These 3-axis mills feature a 20-tool carousel and can hit spindle speeds up to 8,100 RPM. Ideal for small yet precise parts.
Applications: Perfect for training students in basic CNC operations, creating prototypes for research, and fabricating intricate mechanical components.
Haas UMC-750ss (5-Axis)
Overview: Equipped with a dual-axis trunnion table, this advanced machine allows for +120° to -35° tilt and 360° rotation. It’s designed for highly complex geometries.
Applications: Ideal for aerospace components, medical device prototypes, or any intricate design requiring simultaneous multi-axis machining—giving students exposure to cutting-edge production methods.
Haas VF4SS
Overview: Known for high-speed performance, the VF4SS offers a 12,000-RPM spindle and ultra-fast tool changes.
Applications: Great for high-volume production runs and efficiency-focused workflows, teaching students about optimizing cycle times and productivity.
Haas VF5XT
Overview: This machine boasts extended travel, making it perfect for large-scale parts such as molds or oversized prototypes.
Applications: Used for automotive body molds, large research prototypes, or custom industrial components, giving teams the space they need for big ideas.
Haas ST-20Y CNC Lathe
Overview: A versatile lathe with milling and drilling capabilities. It’s user-friendly, thanks to intuitive controls.
Applications: Used to produce turned parts like shafts, bushings, and other cylindrical components—a staple in mechanical and automotive engineering.

Cutting Equipment
What Is Cutting Equipment?
Cutting equipment utilizes high-pressure water, plasma, or electric discharge to shape materials with extreme precision. These machines handle everything from artistic metalwork to industrial-grade fabrication.
IDEELab's Cutting Equipment
Flow Echojet 1313 Waterjet
Overview: An enclosed, quieter system that uses high-pressure water mixed with abrasive material to cut through thick metals and craft intricate patterns.
Applications: Architectural elements, artistic designs, and industrial components requiring smooth, precise edges.
Fanuc Wire EDM Alpha 1
Overview: Uses electrical discharges to carve complex shapes from conductive materials—essential for tool and die-making.
Applications: Creating dies, molds, and precision parts for industries like aerospace or micro-manufacturing.
STV SparX 505 Plasma CNC
Overview: Suited for large-scale metalwork, this plasma cutter can handle steel plates up to 1.5 inches thick with rapid cutting speeds.
Applications: Perfect for heavy-duty fabrication such as construction components, agricultural machinery parts, and industrial frameworks.

Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
What Is Additive Manufacturing?
Unlike subtractive methods that remove material to form a shape, 3D printing builds objects layer by layer from digital models. It’s excellent for rapid prototyping, custom parts, and complex geometries that traditional machining struggles to create.
IDEELab's Additive Manufacturing
Bambu Lab 3D Printers (X1C, P1S, X1E)
Overview: High-precision desktop FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) printers capable of efficiently producing intricate prototypes.
Applications: Used extensively by student teams for robotics competitions, product design, and functional prototypes in research projects.

Measurement & Scanning
Why Measurement & Scanning?
These tools ensure parts meet exact specs by comparing physical objects to their digital CAD models. Accurate metrology is critical for quality control, reverse engineering, and validating research prototypes.
IDEELab's Measurement and Scanning
Keyence VL-700 3D Scanner
Overview: A high-precision scanner that captures detailed point-cloud data of physical parts.
Applications: Reverse engineering, troubleshooting machining errors, and verifying dimensional accuracy against design tolerances.

Welding Equipment
What Is Welding Equipment Used For?
Welding melts and fuses materials, typically metals, creating strong joints essential in construction, automotive, and structural projects. It also gives students real-world, hands-on experience in fabrication.
IDEELab's Welding Equipment
Lincoln Electric Welding Station
Overview: A comprehensive station outfitted with multiple welding systems (e.g., MIG, TIG, Stick) for teaching and advanced project work.
Applications: Student projects requiring frames or chassis, structural assemblies for research, and skill-building workshops on various welding processes.
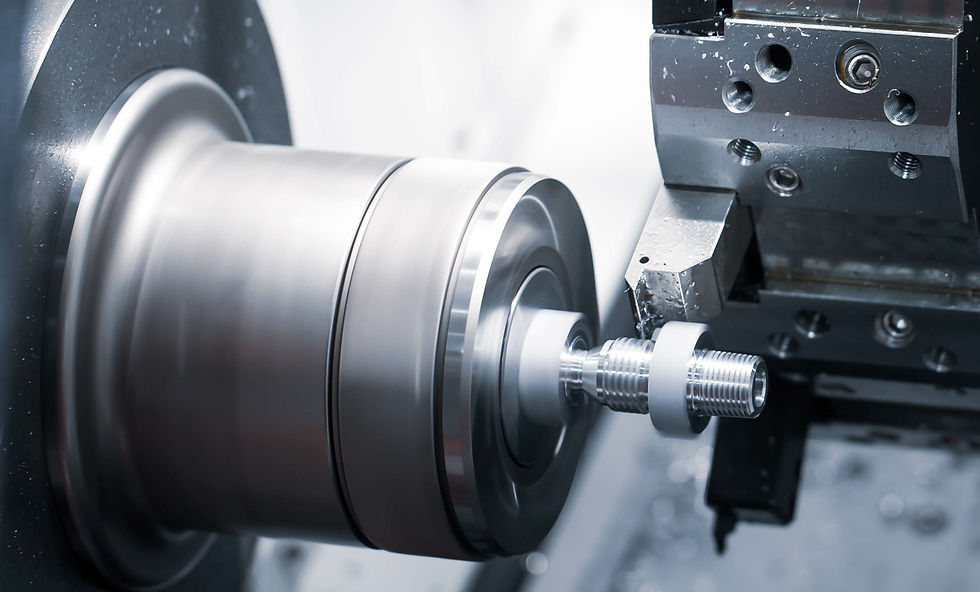
Manual Equipment
Why Manual Machines?
While CNC technology dominates modern manufacturing, manual machining remains a cornerstone of engineering education. It provides foundational skills, helping students understand the mechanics of cutting forces, feeds, and speeds on a personal level.
IDEELab's Manual Equipment
Manual Lathes (4 Units)
Overview: Ideal for small, quick-turnaround machining tasks, letting students learn basic turning operations.
Applications: Creating cylindrical components like rods or bushings, and teaching first-year engineering students the fundamentals of machining.
Manual Mills (5 Units)
Overview: Perfect for flat or contoured surfaces, these mills require hands-on control, reinforcing a strong understanding of tooling and material properties.
Applications: Producing prototypes, fixtures, or teaching the basics of milling operations to newcomers in engineering.
Why It All Matters
IDEELab’s diverse array of machinery isn’t just about having the latest technology—it’s about empowering students and researchers to realize their ideas from concept to completion. By offering CNC machining, cutting tools, additive manufacturing, precision scanning, welding stations, and manual machines all under one roof, the lab provides:
Hands-On Learning: Students gain real industry skills, from programming CNC paths to welding frames.
Efficient Prototyping: Researchers rapidly validate design concepts, iterate, and refine with minimal downtime.
Multidisciplinary Collaboration: Multiple engineering disciplines collaborate seamlessly, reflecting real-world design processes.
Innovation Culture: Access to advanced tools fosters creative thinking, pushing boundaries in both education and research.
Ready to See the Machines in Action?
If you’re interested in witnessing these tools firsthand:
Follow us on social media for video demonstrations, student project showcases, and expert tips from the IDEELab team.
Schedule a visit for an exclusive behind-the-scenes look at the cutting-edge equipment shaping engineering innovation at Mississippi State University.
Enroll in one of our programs to gain hands-on experience and build valuable skills for a future career in the industry.











Comentarios